- Outer space is the area beyond the Earth’s atmosphere.
- It begins at the Kármán line, which is approximately 100 km above sea level.
-
- Outer space is a vacuum, meaning it is empty of matter.
- It is also extremely cold, with temperatures averaging around -270 degrees Celsius.
- The first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, was launched into outer space in 1957 by the Soviet Union.
- The first human to travel into outer space was Yuri Gagarin in 1961.
- The International Space Station (ISS) is a habitable artificial satellite that orbits Earth.
- The Milky Way galaxy, in which Earth is located, is thought to contain around 100 billion planets.
- The nearest galaxy to our own is the Andromeda galaxy, located about 2.5 million light-years away.
- The largest known structure in the universe is the Hercules-Corona Borealis Great Wall, a galaxy cluster that is approximately 10 billion light-years across.
- Outer space is filled with a variety of particles, including cosmic rays and hydrogen.
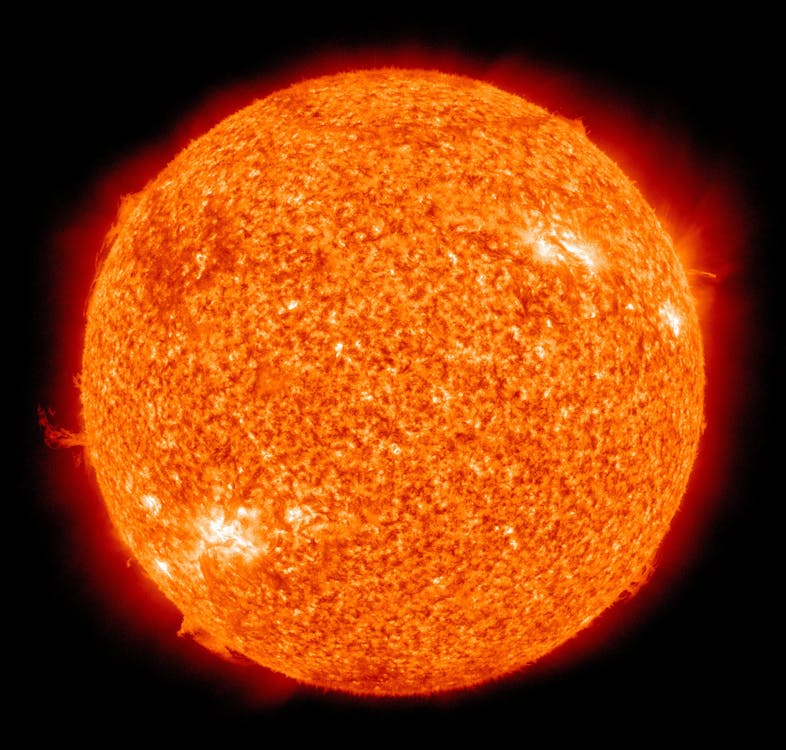
- The Sun is a star located at the center of the solar system, and is the closest star to Earth.
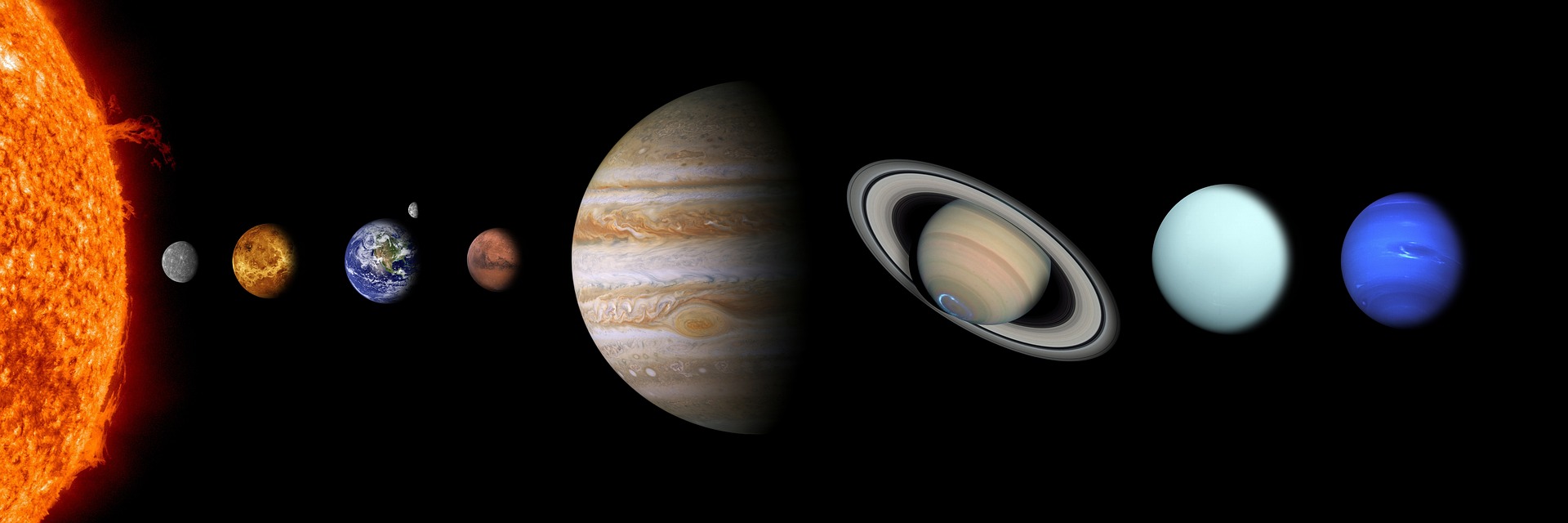
- The solar system is made up of the Sun and all the objects that orbit it, including planets, moons, asteroids, and comets.
- The asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter, is home to millions of asteroids of various sizes.
- There are 8 planets in the solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
- The Kuiper belt is a region of the solar system beyond Neptune that is home to many small, icy objects, including Pluto.
- The heliosphere is the region of space influenced by the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emitted by the Sun.
- The Oort cloud is a hypothetical cloud of comets thought to surround the solar system.
- Dark matter and dark energy are thought to make up most of the universe’s mass and energy, respectively.
- The Big Bang theory is the most widely accepted explanation for the origin of the universe, which is estimated to be around 13.8 billion years old.
- The Hubble Space Telescope, launched in 1990, has provided us with stunning images of distant galaxies and helped us to better understand the universe.
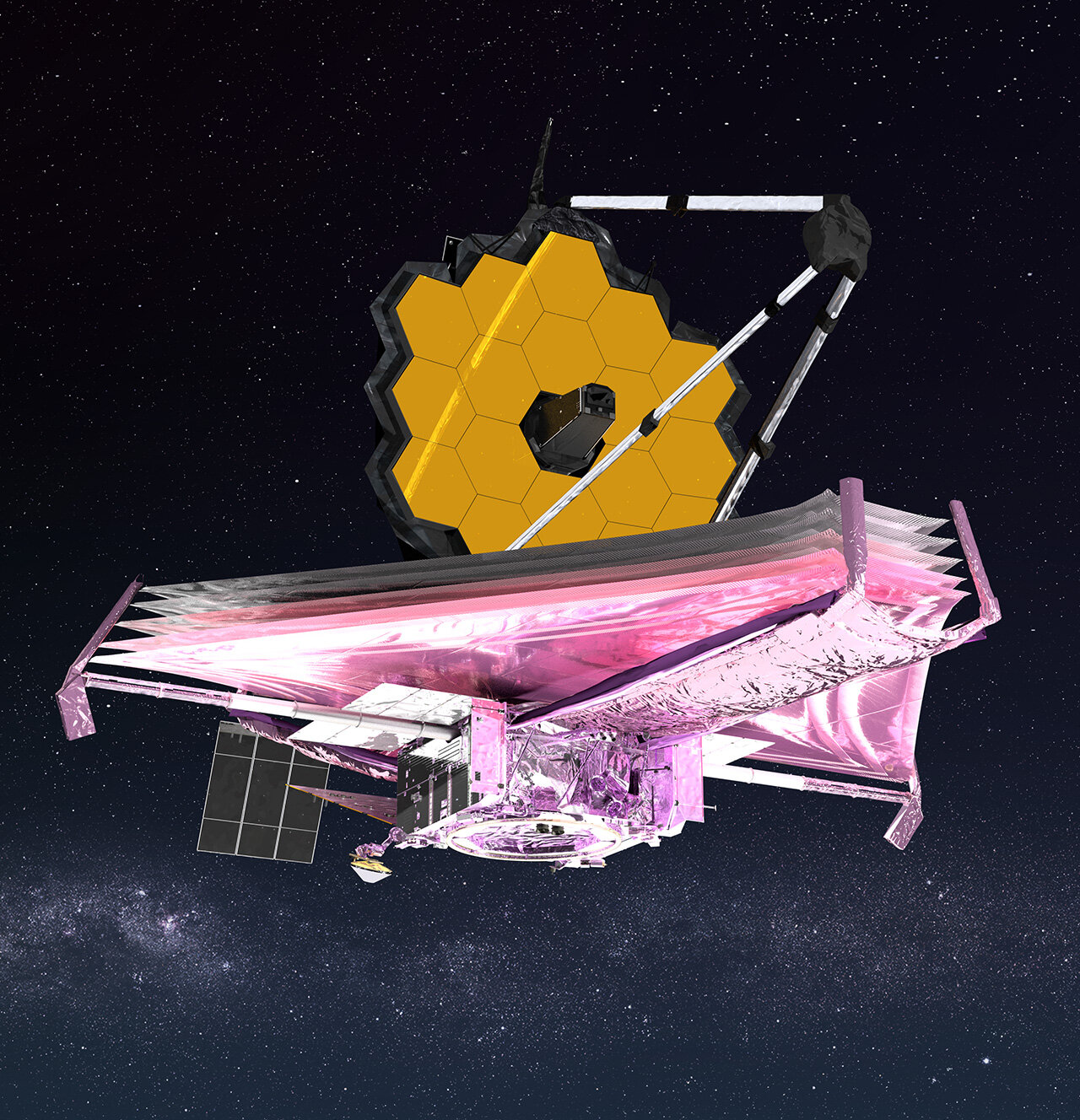
- The James Webb Space Telescope, set to launch in 2021, will be able to observe some of the earliest galaxies in the universe and study the formation of stars and planetary systems.
- The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft, launched in 1977, are currently the most distant human-made objects, having traveled beyond our solar system.
- The Apollo program, which ran from 1961 to 1975, was the first successful manned mission to the Moon.
- The International Space Station is a collaboration between NASA, the Russian Space Agency, and other space agencies from around the world.
- The Moon is the Earth’s only natural satellite, and it is about 384,400 kilometers away from the Earth.
- The planet Mars is known to have the largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons, and the longest canyon, Valles Marineris.
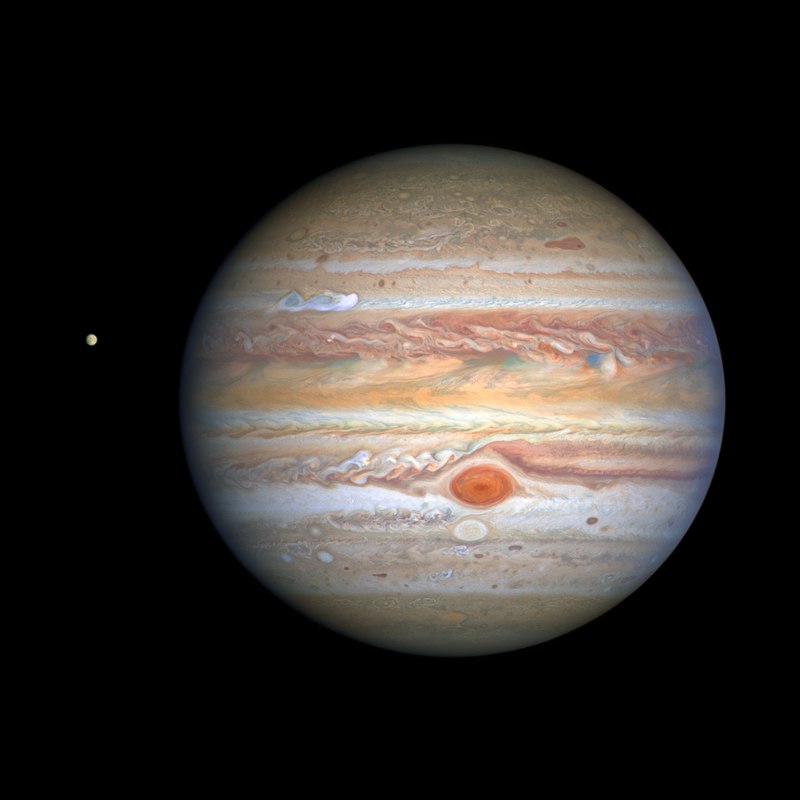
- The planet Jupiter has the largest known planetary atmosphere, and its famous Great Red Spot is a gigantic storm larger than the size of Earth.
- Saturn’s rings are made up of ice particles, ranging in size from tiny grains to large chunks several meters across.
- Uranus and Neptune are known as “Ice Giants” because they are composed mostly of ice and rock, with thick atmospheres of hydrogen and helium.
- The Kuiper Belt is home to many dwarf planets such as Pluto, Eris, and Haumea.
- The asteroid belt is thought to be the remains of a planet that failed to form due to the gravitational influence of Jupiter.
- The nearest star to Earth, other than the Sun, is Proxima Centauri, located 4.22 light-years away.
- The Milky Way galaxy is thought to contain around 400 billion stars.
- The constellation Orion is home to some of the most famous and easily recognizable stars and nebulae, such as the Orion Nebula and Betelgeuse.
- Black holes are extremely dense regions of space with a gravitational pull so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape.
- The cosmic microwave background radiation is a faint glow of light that fills the universe, thought to be a remnant of the Big Bang.
- The study of outer space is known as astronautics or space science.
- The first privately-funded spacecraft to reach orbit was SpaceShipOne, which flew in 2004.
- The study of the origins of the universe, galaxies, stars, and planets is known as cosmology.